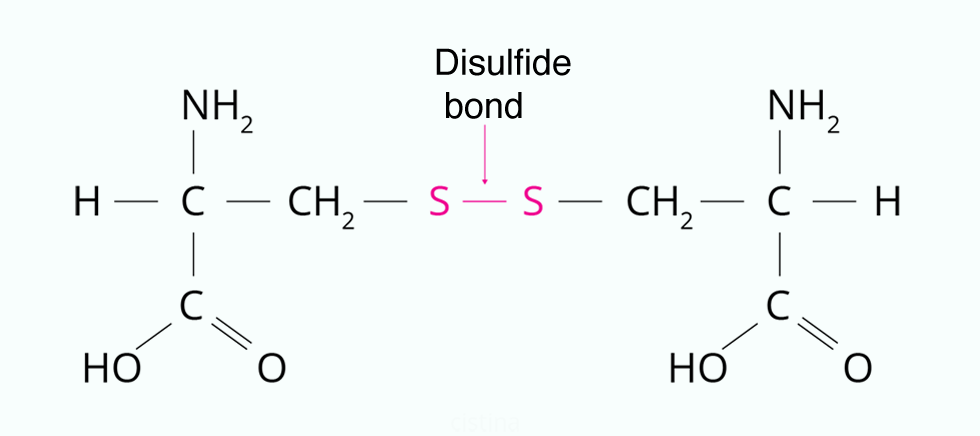
Disulfide bonds are covalent bonds formed between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues in a protein tertiary structure. Cysteine is an amino acid containing a thiol group (-SH). When two cysteine residues come close together in a protein’s tertiary or quaternary structure, the sulfur atoms can undergo an oxidation reaction, resulting in the formation of a disulfide bond (-S-S-). hey act like molecular “safety pins,” keeping parts of the polypeptide firmly attached to one another.