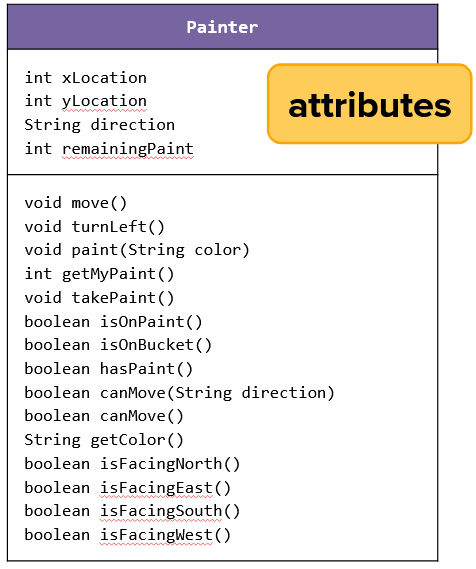
An instance variable is a variable defined in a class that represents an attribute of an object.
Declaring an Instance Variable
private int xLocation;
- ”private” sets the access of the instance variable to private so it cannot be accessed from outside of the class.
- ”int” defines the data type for the instance variable.
- ”xLocation” gives name for the instance variable.
boolean - true or false int - whole numbers, like 7 or 6784 double - decimal numbers, like 2.5 or 92.81 String - a sequence of characters, like “purple”
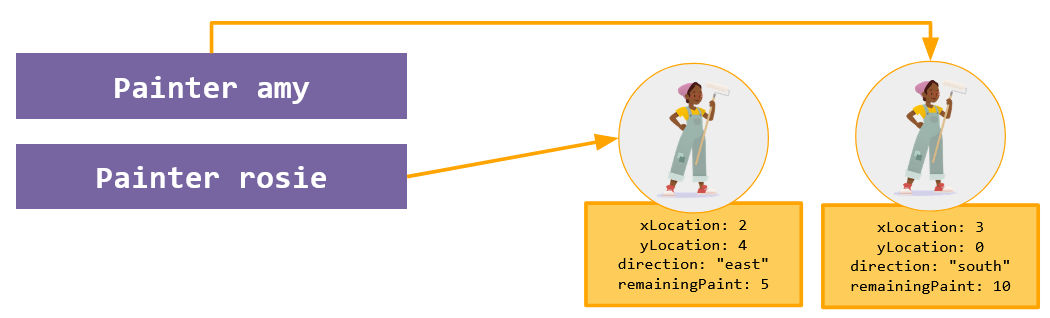
When an object is instantiated, it gets its own copy of the instance variables.
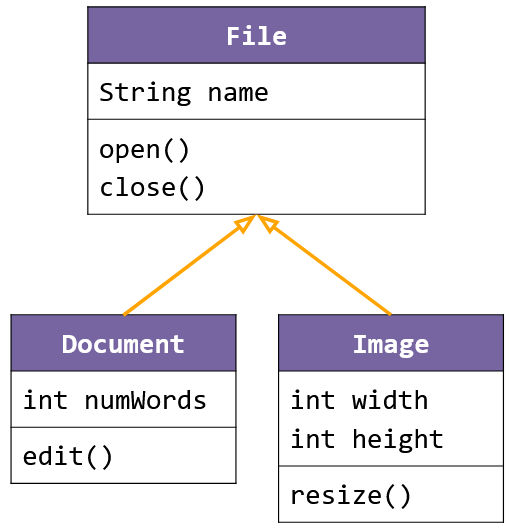
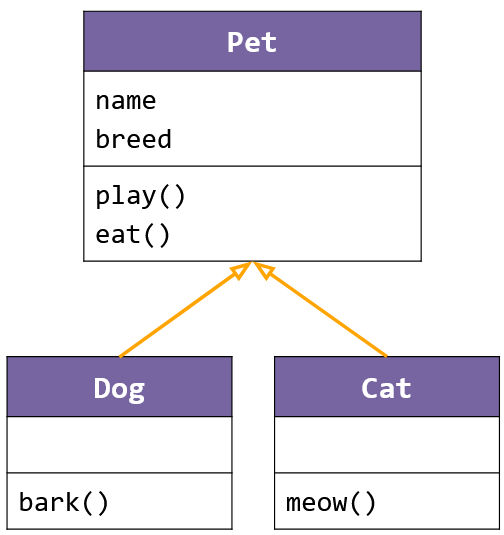
Inheritance is an object-oriented programming principle where a subclass inherits the attributes and behaviors of a superclass.
Encapsulation is an object-oriented programming concept where the instance variables of a class are hidden from other classes and can be accessed only through the methods of the class.
An access modifier is used to set the visibility of classes, variables, constructors, and methods.
public - visible to all classes in a program private - visible to only inside the class
Inheritance helps in making our code reusable and keeping it DRY. The DRY principle is a software development principle that stands for “Don’t Repeat Yourself” which aims to reduce repetition in code.
To refactor code to improve the readability, reusability, or structure of program code without altering its functionality.