Introduction The nucleus is not the only organelle that contains DNA. DNA can also be found in the chloroplast of plant cells and the mitochondria.
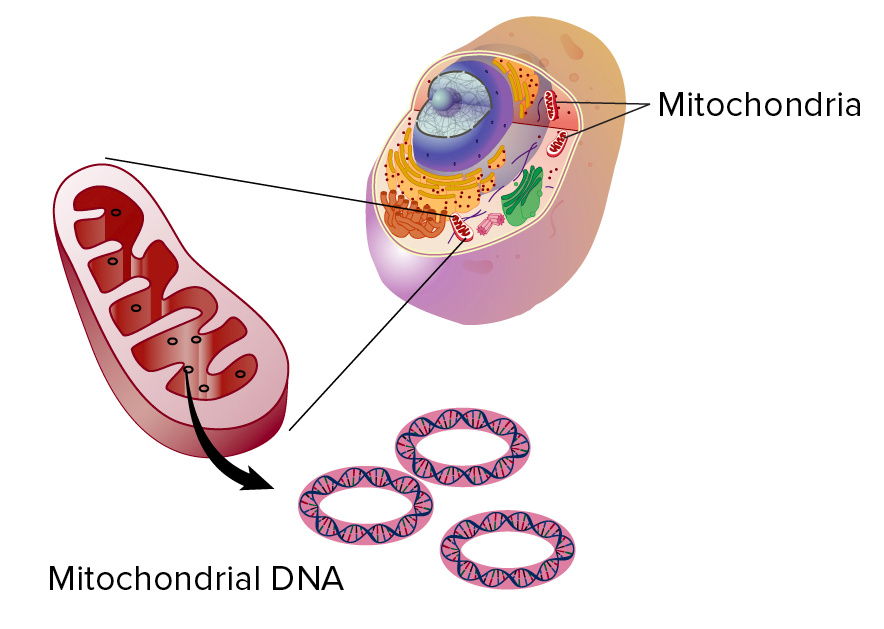
Mitochondrial and Chloroplast DNA The DNA molecules found in mitochondria and chloroplasts are small and circular, much like the DNA of a typical bacterium. There are usually many copies of DNA in a single mitochondria or chloroplast.
How is non-nuclear DNA inherited?
- High copy number - A mitochondrion or chloroplast has multiple copies of its DNA. As a result, cells usually have thousands of mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA.
- Random segregation - Mitochondria and chloroplasts are randomly distributed to daughter cells during mitosis and meiosis.
- Single-parent inheritance - Non-nuclear DNA is often inherited uniparentally, meaning that offspring get DNA only from the male or the female parent, not both. In humans, for example, children get mitochondrial DNA from their mother (but not their father).
Chloroplast Inheritance As the zygote undergoes many rounds of mitosis to form an embryo and then a plant, the chloroplasts also divide and are distrusted randomly to daughter cells at each division.
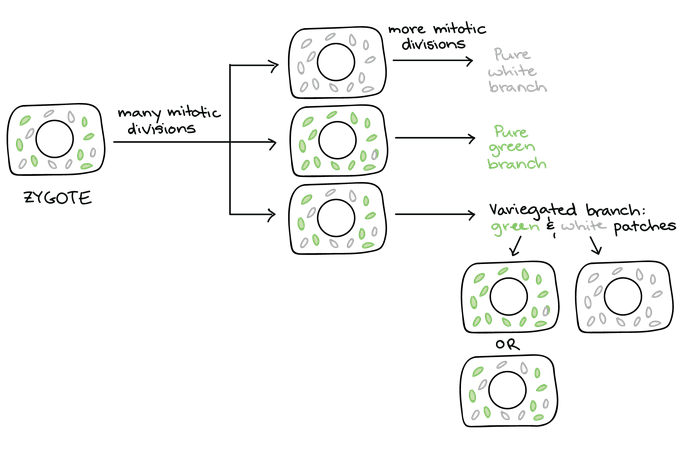
Over the many cell divisions, some cells will have a pure set of normal chloroplasts (green patches) while others get a pure set of nonfunctional chloroplasts )white patches). Others yet will have a mix of normal and nonfunctional chloroplasts (mixed patches).
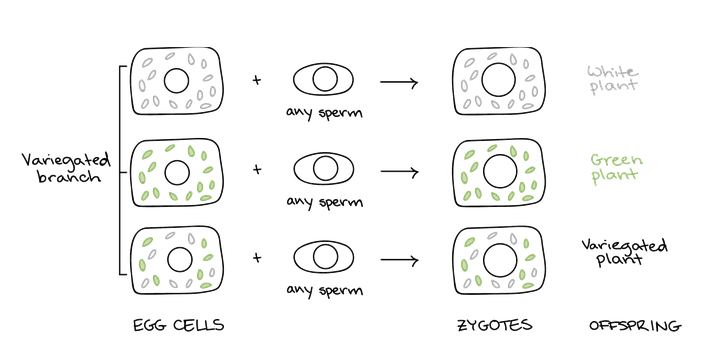
A branch that’s pure green will make egg cells with green chloroplasts that give rise to pure green offspring. Similarly, a branch that’s pure white will make egg cells that contain only white chloroplasts and will give rise to pure white offspring.
If a branch is variegated, the cell types may give rise to egg cells that lead to green, white, or variegated offspring in unpredictable ratios.
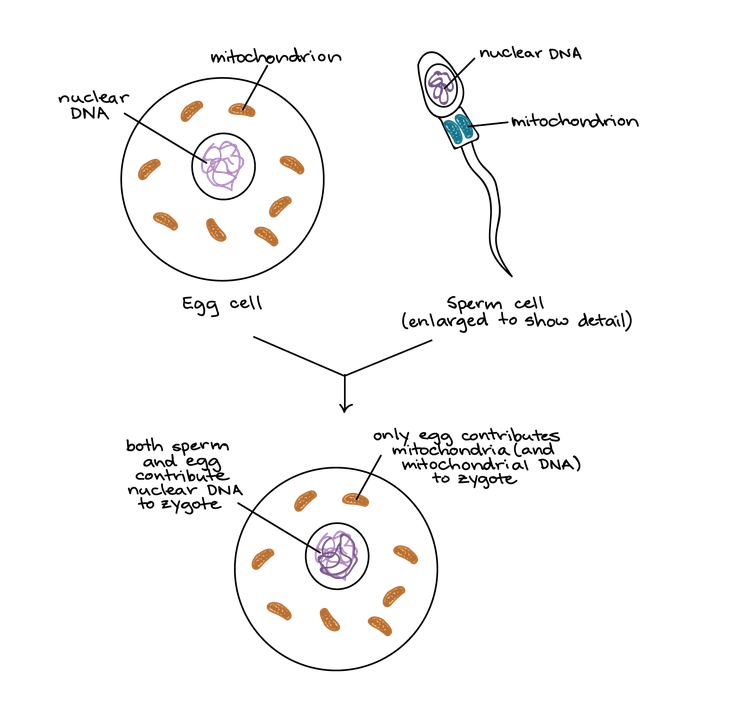
Mitochondrial Inheritance Mitochondria, like chloroplasts, tend to be inherited from just one parent. In the case of humans, it is the mother who contributes mitochondria to the zygote. Sperm do contain mitochondria, but they are not usually inherited. There have been cases but this is extremely rare.
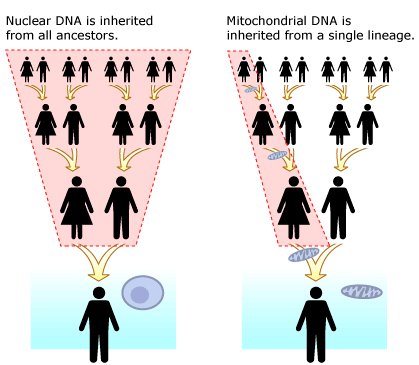
Because mitochondria are inherited from a person’s mother, they provide a way to race matrilineal ancestry. This is different for nuclear DNA, which is inherited from all ancestors.
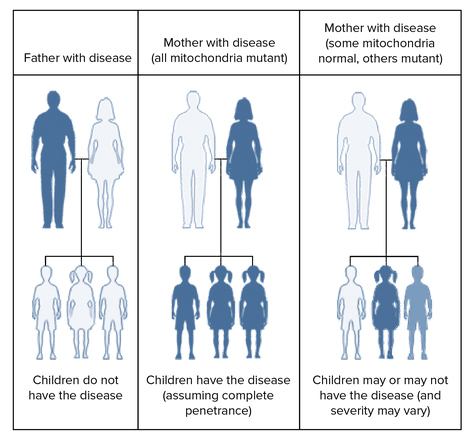
Mitochondrial Mutations and Human Disease Mutations in mitochondrial DNA can lead to human genetic disorders. Genetic disorders caused by mitochondrial mutations are not transmitted from fathers to children, because mitochondria are only provided by the mother. Instead, they are transmitted from mothers to children in one of the following ways:
- A person with a disease caused by a mitochondrial mutation may lack normal mitochondria. In this case, an affected mother will aways pass on mutation-bearing mitochondria to her children.
- A mitochondrial disorder may occur when a person has a mix of normal and abnormal mitochondria in her body. In this case, normal and mutation-bearing mitochondria may go randomly into eggs during meiosis. Some children with a large proportion of mutant mitochondria may have a severe disease, while those with few mutant mitochondria may have mild or no disease.