Adhesion is the attraction of molecules of one kind for molecules of a different kind, and it can be quite strong for water, especially with other molecules bearing positive or negative charges. This is due to water’s polarity attracting it to substances that have charges.
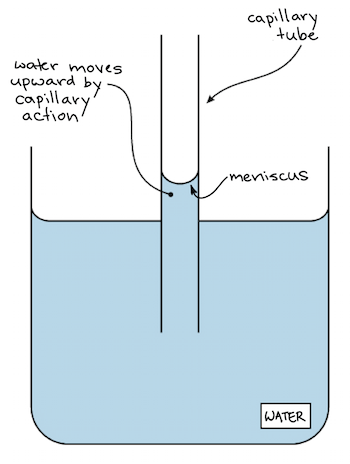
For instance, adhesion enables water to “climb” upwards through thin glass tubes (called capillary tubes) placed in a beaker of water. This upward motion against gravity, known as capillary action, depends on the attraction between water molecules and the glass walls of the tube (adhesion), as well as on interactions between water molecules (cohesion).
The water molecules are more strongly attracted to the glass than they are to other water molecules (because glass molecules are even more polar than water molecules). You can see this by looking at the image below: the water extends highest where it contacts the edges of the tube, and dips lowest in the middle. The curved surface formed by a liquid in a cylinder or tube is called a meniscus.