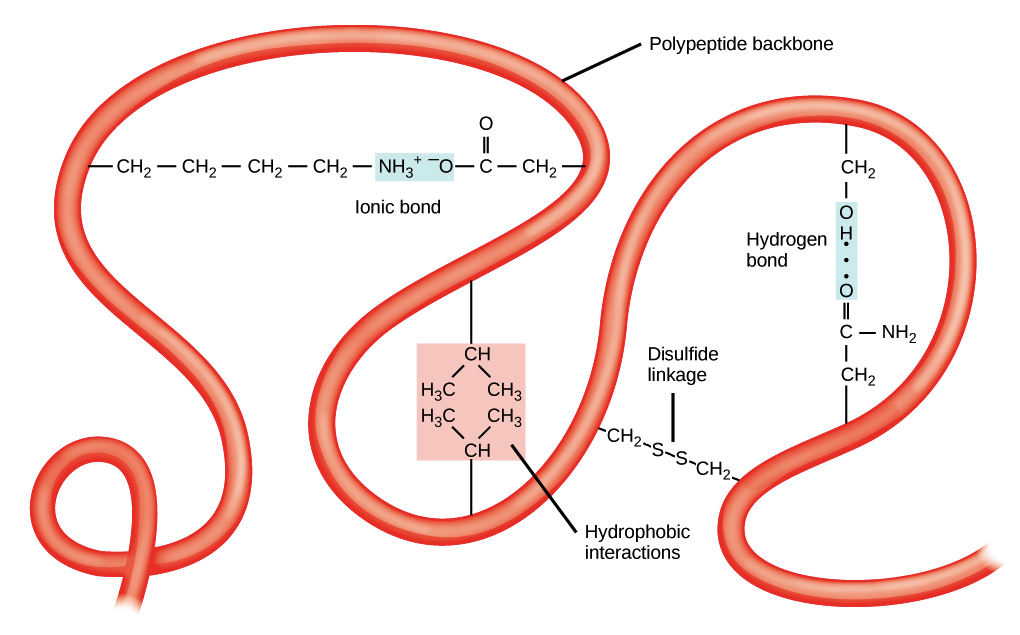
The protein tertiary structure is a protein structure and is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain “backbone” with one or more protein secondary structures. The tertiary structure is primarily due to interactions between the R groups of the amino acids that make up the protein.
R group interactions that contribute to tertiary structure include hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces – basically, the whole gamut of non-covalent bonds. For example, R groups with like charges repel one another, while those with opposite charges can form an ionic bond. Similarly, polar R groups can form hydrogen bonds and other dipole-dipole interactions. Also important to tertiary structure are hydrophobic interactions, in which amino acids with nonpolar, hydrophobic R groups cluster together on the inside of the protein, leaving hydrophilic amino acids on the outside to interact with surrounding water molecules.
Finally, there’s one special type of covalent bond that can contribute to tertiary structure: the disulfide bond. Disulfide bonds, covalent linkages between the sulfur-containing side chains of cysteines, are much stronger than the other types of bonds that contribute to tertiary structure. They act like molecular “safety pins,” keeping parts of the polypeptide firmly attached to one another.